PIGMENTATION TREATMENT
Hyperpigmentation is a medical term used to describe darker patches of skin. These patches result from excess melanin production, which can be caused by everything from acne scars and sun damage to hormone fluctuations.
If you’re dealing with hyperpigmentation, know that you aren’t alone. Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition, and there are a number of different treatment options available depending on severity, skin type, etc.
Keep reading to learn more about your options, including products you can try at home and what to expect from procedures:


SKIN LIGHTENING TREATMENT
Lightening creams are over-the-counter (OTC) treatments that work with select ingredients to help decrease pigmentation. They’re usually applied once or twice a day to help lighten the skin over time.
Common ingredients found in OTC lightening products include:
- hydroquinone
- licorice extract
- N-acetylglucosamine
- vitamin B-3 (niacinamide)
Lightening creams or gels work best for flat spots, such as melasma or age spots. They’re effective for patches of discoloration on most skin types.
OTC products are accessible (and sometimes more affordable) options for hyperpigmentation, but these can take longer than procedures.
FACE ACID
Face acids, or skin acids, work by exfoliating, or shedding, the top layer of your skin. Whenever you exfoliate your skin, new skin cells emerge to take the place of the old ones. The process helps even out your skin tone and makes it smoother overall. Some examples are the following:
- alpha hydroxy acids, such as glycolic, lactic, citric, malic, or tartaric acid
- azelaic acid
- kojic acid
- salicylic acid
- vitamin C (in the form of l-ascorbic acid)
WHO SHOULD TRY THIS ?
Face acids work well for mild hyperpigmentation on fairer skin tones.

RETINOIDS
Derived from vitamin A, retinoids are among some of the oldest OTC skincare ingredients used. Their small molecular structure allows them to penetrate deep into the skin and treat the layers below your epidermis.
WHO SHOULD TRY THIS ?
OTC retinoids may be safe for all skin tones, but you should double-check with your dermatologist if you have darker skin and plan on using these products long term.
It’s also important to note that retinoids are more often used to treat wrinkles than hyperpigmentation. This means that retinoids may not be the best first-line treatment.
CHEMICAL PEEL
A chemical peel uses acids at stronger concentrations to treat the desired area of skin. They reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation by removing the epidermis. Deeper versions may also penetrate the middle layer of your skin (dermis) to produce more dramatic results. Various peels are used depending on the depth of pigmentation & desired results.
If you’re out in the sun on a regular basis, chemical peels may not be the best treatment option for you. Chemical peels cause your skin to be more sensitive to the sun’s rays. If you don’t adequately apply sunscreen and use other UV protection, the sun may worsen your hyperpigmentation. You’ll need to take extra precautions for at least a couple of days after your last chemical peel. Ideally, avoid outdoor activities a few days after the chemical peel procedure.
WHO SHOULD TRY THIS ?
Chemical peels may work if you have:
- age spots
- sun damage
- melasma
They also work best for fairer skin tones, and they may provide faster results than face acid products.

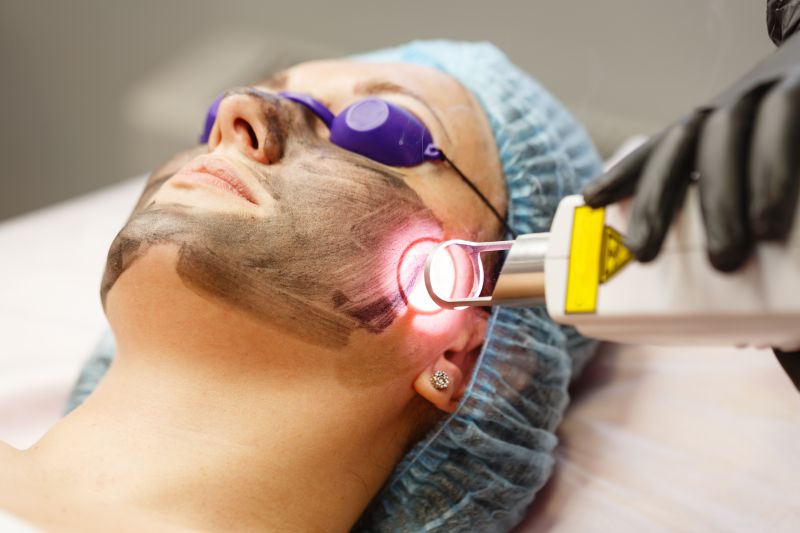
LASER PEEL (SKIN RESURFACING)
A laser peel (resurfacing) treatment uses targeted beams of light to reduce hyperpigmentation.
There are two types of lasers: ablative and non-ablative. Ablative lasers are the most intense, and they involve removing layers of your skin. Non-ablative procedures, on the other hand, target the dermis to promote collagen growth and tightening effects.
Ablative lasers are stronger, but they may cause more side effects. Both destroy elements in your skin to ensure that new skin cells grow back tighter and more toned.
MICRODERMABRASION
Microdermabrasion is a procedure used to treat hyperpigmentation that affects the epidermis only (superficial scarring).
During the procedure, your dermatologist will use a handheld tool with a wire brush or other abrasive attachment. The tool is then swiped across your skin to rapidly — but gently — to remove the epidermis. You may need multiple sessions to achieve your ideal result.
WHO SHOULD TRY THIS ?
Microdermabrasion works best on superficial scars. It also works well for people with fairer skin.
- No matter what treatment you ultimately choose, it’s important to protect your skin from further sun damage and hyperpigmentation. Wearing sunscreen every day is a must. You should apply sunscreen every morning — even when it’s cloudy! — and reapply as needed throughout the day. Be sure to use a sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher.

