
ROSACEA
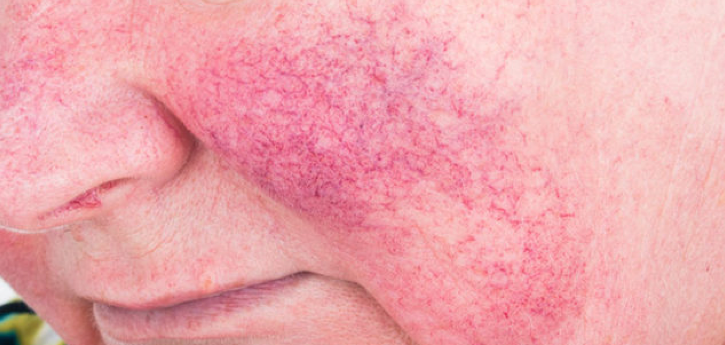
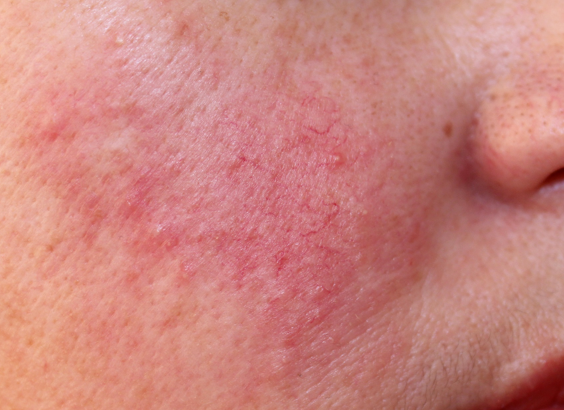
Rosacea is a chronic, non-contagious, inflammatory skin condition affecting about 14 million Americans, usually between the ages of 30 and 60. It is characterized by a flushing redness of the cheeks, chin, nose, and forehead, and may produce small, red, pus-filled bumps or pustules. Rosacea appears to affect more fair-skinned people than dark, though it can affect any skin type.
As the condition progresses, the flushing becomes more persistent and noticeable. In severe cases, most of the face is affected. The disorder affects more women than men, but is generally more severe for men. Sometimes, permanent facial changes can occur for men, such as thickening of the skin on the nose.
CAUSES & TREATMENT
Causes: The cause of rosacea is currently unknown. However, researchers have several ideas about what may cause rosacea. Often, rosacea runs in the family, suggesting a genetic predisposition combined with environmental factors may be the cause. It could also be caused by a disorder of the blood vessels that triggers them to swell, leading to flushing.
Treatment: There is no known cure for rosacea, but treatment is available, and Last Name(s) can help you determine which method is best for you. Typically, improvements should be noticed within 1 to 2 months of treatment.
Topical Medications
Medications you apply to your skin once or twice daily, such as antibiotics, benzoyl peroxide, and azelaic acid can help reduce inflammation and redness. These creams and lotions are generally used in combination with other treatment, such as oral medication.
Oral Antibiotics
Oral antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce inflammation. Oral antibiotics tend to work faster than topical antibiotics, so they may be beneficial for severe cases, or if the physical appearance is interfering with the patient’s normal activities.
Isotretinoin (Accutane)
Isotretinoin is a very strong oral medication usually used to treat cystic acne. In some extremely severe cases of rosacea, isotretinoin may be prescribed if all other methods of treatment fail. Isotretinoin works by inhibiting the production of oil by sebaceous glands. Because isotretinoin has many serious side effects, Last Name(s) will closely monitor your use.
Surgery
Enlarged blood vessels may become permanent. If this occurs, surgical options such as laser therapy may help reduce the visibility of these vessels, and removal of extra tissue buildup around the nose can improve overall appearance.
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent rosacea, but you can take steps to reduce or control symptoms. For example:
Remember to continue your treatment plan even after rosacea clears or improves to ensure it does not reappear.
Avoid rosacea triggers such as sun exposure, extreme temperatures, spicy food and alcohol.
Always be gentle with your skin. Only use mild cleansers, and avoid products containing irritants such as alcohol.
